Bioluminescent lighting could be a sustainable alternative to LEDs by using living organisms like engineered bacteria or plants to produce natural light. This method relies on biochemical reactions, which don’t need electricity and generate less pollution. While current brightness levels are lower than LEDs, ongoing research aims to improve their output and color. If you want to discover how this eco-friendly tech might reshape lighting in the future, keep exploring its potential.
Key Takeaways
- Bioluminescent lighting is energy-efficient and relies on organic biological processes, reducing electricity consumption compared to LEDs.
- It offers sustainable, self-replenishing illumination without the need for batteries or wiring, unlike traditional LED systems.
- Currently producing lower luminance levels, bioluminescent lighting is suitable for ambient or decorative applications rather than high-brightness needs.
- Advances in engineering luciferases and organisms could enhance brightness, color, and durability, making bioluminescent lighting more competitive.
- It provides environmentally friendly, low-pollution lighting that integrates seamlessly into natural settings, supporting sustainable development goals.
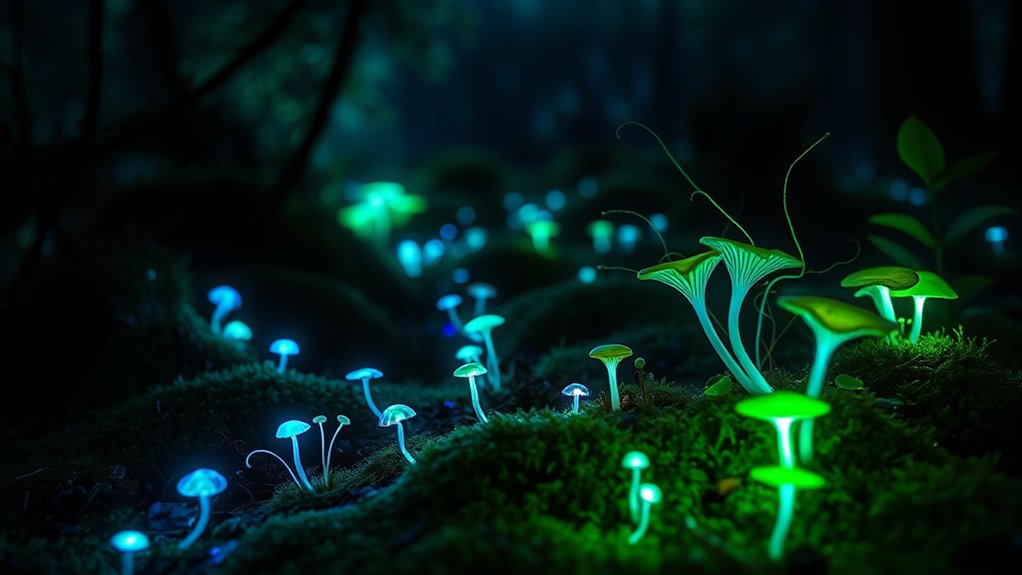

Bioluminescent lighting harnesses the natural ability of certain organisms to produce light through a biochemical reaction. This process involves an organic substrate called luciferin and an enzyme called luciferase. When these components interact, they oxygenate luciferin, creating an excited molecule that releases light as it returns to a stable ground state. Unlike fluorescent or phosphorescent lights, bioluminescence doesn’t need prior light absorption, making it a unique and efficient source of illumination. Some luciferases need additional cations like magnesium or calcium ions to stabilize the oxygenated luciferin, ensuring a consistent glow. Despite extensive research, scientists haven’t fully unraveled all the biochemical mechanisms behind bioluminescence, which limits its widespread application. Still, advances in understanding and engineering these biological systems are opening new possibilities. Understanding biochemistry is crucial for improving bioluminescent technologies and expanding their applications.
You can find marine bacteria, such as Aliivibrio fischeri, commonly used in bioluminescent lighting systems. These bacteria are stored in saltwater and used in biofixtures, creating a natural glow that’s both mesmerizing and sustainable. Companies like Glowee are working to enhance bacterial bioluminescence, making the glow brighter and longer-lasting. Researchers are also developing ways to tweak marine luciferases, allowing them to change the color of the emitted light through bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET). This engineering effort aims to produce customizable lighting solutions. Additionally, efforts are underway to develop bioluminescent plants that could serve as self-lighting, electricity-free lamps. These plants would absorb CO₂, potentially reducing greenhouse gases while providing sustainable illumination.
Bioluminescent lighting offers significant energy-saving benefits. Since it doesn’t rely on electricity to produce light, it can drastically cut energy consumption compared to LEDs. The process of producing bioluminescent materials also consumes less energy than manufacturing energy-efficient LED lights. If properly maintained, bioluminescent organisms could serve as renewable, sustainable light sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. Their gentle, natural glow minimizes light pollution, making them ideal for urban environments seeking eco-friendly solutions. Because biological sources are self-replenishing, they can provide continuous illumination without needing batteries or electrical wiring—offering a promising alternative to traditional lighting.
Currently, bioluminescent systems operate similarly to aquariums and can run indoors year-round if bacteria are regularly fed and maintained. Some public installations, like curb lanterns, have successfully tested bioluminescent lighting in urban settings. While outdoor applications for street lighting are still under development, they hold potential for reducing energy costs and environmental impact. However, a key challenge remains: bioluminescent lighting typically produces a lower luminous intensity—about 15-20 lumens per square meter—compared to 111 lumens from standard LED setups. Despite this, the minimal electricity needed makes bioluminescence attractive for off-grid or low-power applications, especially in areas with limited access to conventional power sources.
In the end, bioluminescent lighting could revolutionize urban and outdoor illumination. Its ability to cut energy use, reduce pollution, and create a gentle, natural glow aligns with growing environmental concerns. As research progresses, engineered bioluminescent organisms and plants might become common fixtures, offering sustainable, self-sufficient lighting solutions that blend seamlessly into the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Bioluminescent Lighting Last Compared to LEDS?
You wonder how long bioluminescent lighting lasts compared to LEDs. While LEDs shine steadily for at least 50,000 hours, bioluminescent light only lasts hours to days before needing renewal. LEDs offer a predictable, long-lasting solution with minimal maintenance, whereas bioluminescent systems require frequent reactivation or replacement due to biological limits. Despite current challenges, ongoing research aims to improve bioluminescent longevity, but it still falls short of LED durability.
Are Bioluminescent Lights Energy-Efficient?
You’re wondering if bioluminescent lights are energy-efficient, and the answer is yes. They convert chemical energy into light with nearly 100% efficiency, much better than incandescent bulbs and LEDs. Since they produce “cold light,” they waste very little energy as heat. Plus, they don’t need electricity, reducing energy consumption and environmental impact. However, their brightness and longevity still need improvement to match traditional lighting, but their biochemical efficiency is promising.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Bioluminescent Lighting?
Think of bioluminescent lighting as a gentle glow from nature’s own lanterns, casting a soft light that doesn’t disturb the night’s natural harmony. You’ll find it reduces energy use and lowers pollution, helping the environment breathe easier. It minimizes light pollution, protecting wildlife and ecosystems. But, be cautious—some organisms can cause harmful algal blooms or ecological risks. With mindful use, it offers a promising, eco-friendly glow for our world.
Can Bioluminescent Lighting Be Used Outdoors in All Climates?
You wonder if bioluminescent lighting works outdoors in all climates. While it offers eco-friendly benefits, environmental factors like extreme temperatures, humidity, UV exposure, and seasonal changes can limit its effectiveness. These conditions may reduce light output or harm organisms. To succeed outdoors, you’ll need protective housing, climate-specific engineering, and adaptive management. Currently, bioluminescent lighting suits certain environments best, but ongoing research aims to expand its practicality across diverse climates.
How Cost-Effective Is Bioluminescent Lighting for Large-Scale Applications?
You’re wondering how cost-effective bioluminescent lighting is for large-scale use. Currently, it involves high initial costs due to complex production and specialized equipment. However, over time, it can save money through lower energy consumption and reduced maintenance. As innovations improve stability and scalability, and with potential government incentives, bioluminescent lighting could become more economically viable, especially when considering environmental benefits and long-term operational savings.
Conclusion
Imagine walking into a room where the walls glow softly like fireflies dancing in the night. With bioluminescent lighting, you become part of a living, breathing masterpiece, turning darkness into a gentle symphony of light. This revolutionary glow promises to replace harsh LEDs, offering a sustainable, mesmerizing alternative. As nature’s own lanterns, bioluminescent lights could illuminate your world, transforming everyday spaces into enchanted domains where science and magic intertwine seamlessly.