Space-based solar power systems collect sunlight in orbit with large solar arrays, then convert it into energy beams, usually microwave or laser, directed down to Earth. These beams are focused and safe, providing a continuous power source unaffected by weather or night cycles. If you keep exploring, you’ll discover how advances in technology and international efforts are making this innovative energy solution a practical reality for the future.
Key Takeaways
- Space-based solar arrays capture sunlight continuously in geostationary orbit, converting it into electrical energy.
- The energy is transmitted wirelessly via microwave or laser beams directed toward Earth-based receiver stations.
- Precise targeting systems ensure safe and efficient delivery of high-power beams from space to ground.
- Ground stations convert received energy into usable electricity for the power grid.
- This method provides a reliable, weather-independent energy source with minimal environmental impact.
How Space-Based Solar Power Works

Have you ever wondered how solar power from space is collected and transmitted back to Earth? It all starts with understanding orbital mechanics. Satellites in geostationary orbit stay fixed relative to Earth, allowing solar panels to continuously capture sunlight without interruption. These satellites are equipped with large solar arrays that convert sunlight into electricity. To keep these arrays operating efficiently, satellite maintenance is vital—regular adjustments and repairs ensure maximum performance. Because of the vast distance, precise positioning and stable orbits are essential for transmitting energy via microwave or laser beams. Maintaining the satellite’s orbit and health requires sophisticated navigation and control systems, guaranteeing that the collected solar energy is consistently sent back to Earth’s receiving stations for conversion into usable power. Proper maintenance of satellites is also crucial to prevent disruptions in energy transmission.
Components of Space Solar Arrays

Space solar arrays consist of several key components designed to efficiently collect and convert sunlight into usable energy. These components include the solar panels themselves, power conversion systems, and deployment mechanisms. During satellite deployment, you’ll activate the array’s unfolding system to guarantee proper orientation and positioning in space. The solar panels are built for maximum array durability, resisting radiation and temperature fluctuations, which extends their operational lifespan. The power conversion systems transform sunlight into electricity, ready to be transmitted or stored. To optimize performance, every component must withstand harsh space conditions and facilitate smooth satellite deployment. Additionally, the use of sustainable materials in manufacturing helps reduce environmental impact. These elements work together to ensure the array functions reliably over time, maximizing energy collection while maintaining structural integrity in the challenging environment of space.
Wireless Power Transmission Methods
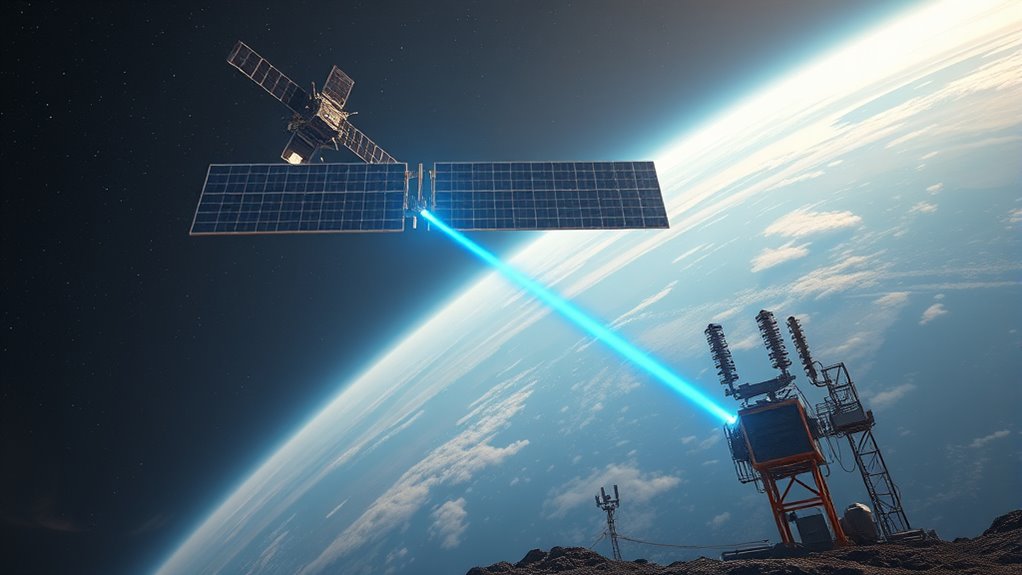

Wireless power transmission methods enable space solar arrays to deliver collected energy to Earth without the need for physical connectors. This process relies on wireless transmission techniques that convert solar energy into energy beams, which can travel across space safely and efficiently. The most promising approach involves using microwave or laser energy beams, directed precisely at receiving stations on Earth. Microwave transmission is well-tested and can carry large amounts of energy with minimal loss, while laser energy beams offer higher focus and efficiency but require advanced targeting systems. These energy beams are designed to be safe for the environment and humans, as they are highly focused and controlled. Implementing precise targeting systems enhances the safety and efficiency of wireless transmission by ensuring energy beams are directed accurately. Wireless transmission guarantees a seamless, continuous flow of power from space to Earth, overcoming the limitations of traditional cable-based methods.
Advantages of Space-Generated Energy

One of the key benefits of space-generated energy is its ability to provide a virtually unlimited and reliable power source. Unlike Earth-based sources, it’s unaffected by weather or daylight cycles, ensuring consistent energy supply. Additionally, space power stations can operate continuously, regardless of space weather phenomena like solar storms that might disrupt terrestrial grids. You also avoid issues caused by orbital debris, which can threaten ground-based infrastructure and complicate terrestrial energy storage. Furthermore, the high efficiency of space-based solar panels ensures maximum energy capture and transmission to Earth.
Overcoming Technical Challenges

Achieving reliable energy transmission from space-based solar power systems involves overcoming several significant technical hurdles. One major challenge is thermal regulation; solar panels and equipment in space must dissipate heat effectively to prevent overheating, which can impair performance and damage components. Developing advanced cooling systems is essential for maintaining ideal operation. Another obstacle is orbital deployment; deploying and maintaining large, precise structures in orbit requires sophisticated engineering to guarantee stability and alignment. Engineers must also address the complexities of launching, assembling, and adjusting these systems in space. Overcoming these technical challenges demands innovation in materials, precise control mechanisms, and efficient deployment strategies, all vital for ensuring that space-based solar power can deliver consistent and safe energy to Earth. Additionally, managing heat dissipation effectively in the harsh environment of space remains a critical area requiring ongoing research and development.
Environmental and Safety Considerations

While space-based solar power offers a promising clean energy source, it also raises important environmental and safety concerns. You must consider orbital debris mitigation to prevent collisions that could create hazardous debris clouds. Implementing strict spacecraft safety protocols ensures the protection of both the solar arrays and other space assets. Additionally, managing the South Beach Tow cast updates can serve as a reminder of the importance of responsible operations and accountability in high-profile projects.
Key considerations include:
- Developing debris removal strategies to minimize space clutter.
- Ensuring safe operation procedures during satellite deployment and maintenance.
- Designing systems to prevent accidental beam misdirection that could harm satellites or terrestrial environments.
Addressing these issues is essential to maintaining a sustainable and safe space environment, reducing risks of collisions, and safeguarding Earth’s safety and ecosystems.
Current Projects and Future Prospects

You can explore how active satellite initiatives are already testing space-based solar power systems. Advances in technology promise to make these projects more efficient and cost-effective in the near future. Additionally, increased policy and funding support could accelerate the deployment of these innovative energy solutions. As these projects progress, technological innovation will play a crucial role in overcoming current limitations and expanding the feasibility of space-based solar power.
Active Satellite Initiatives
Are current satellite initiatives bringing space-based solar power closer to reality? Yes, ongoing projects focus on deploying and maintaining satellites efficiently. These initiatives involve advanced satellite deployment techniques to place power-generating units in orbit. Orbital maintenance plays a vital role in ensuring satellites stay aligned and functional over long periods. To deepen understanding, consider these key points:
- Innovative deployment methods reduce launch costs and increase satellite density.
- Autonomous orbital maintenance systems extend satellite lifespan and reliability.
- Collaboration among international agencies accelerates the development of scalable power satellites.
- Incorporating renewable energy solutions like solar panels into satellite design can improve sustainability and energy output.
These efforts aim to overcome technical challenges, making space-based solar power a practical, sustainable energy source for the future.
Technological Advancements Ahead
Advancements in technology are rapidly shaping the future of space-based solar power, with new projects pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Researchers are making significant progress in increasing solar panel efficiency, enabling more energy to be captured in space. Improved materials and design innovations mean solar arrays can generate power more effectively while reducing weight and cost. Orbital placement also plays a critical role; scientists are exploring *ideal* orbits to maximize sunlight exposure and minimize energy losses during transmission. These technological strides are essential for creating scalable, reliable systems that can deliver consistent power to Earth. As projects evolve, you’ll see more sophisticated, efficient, and cost-effective solutions, bringing us closer to harnessing space-based solar power as a sustainable energy source for the future. AI integration is also increasingly being applied to optimize system performance and predictive maintenance.
Policy and Funding Support
Policy and funding support are crucial for transforming space-based solar power from a promising concept into a practical energy solution. Effective international collaboration can pool resources, share expertise, and accelerate development. Establishing clear regulatory frameworks ensures safe, efficient deployment of satellite systems and power transmission. To advance, consider these key areas:
- Securing government and private sector funding to support research, prototypes, and pilot projects.
- Developing international agreements that facilitate cross-border collaboration and management of space assets.
- Creating regulatory standards that address safety, frequency allocation, and environmental impacts, fostering investor confidence.
- Implementing comprehensive risk management strategies to address potential technical and security challenges.
With strong policy backing, you’ll see more projects move from concept to reality, paving the way for sustainable, space-based energy to reach Earth efficiently and safely.
The Path Toward Practical Implementation

Turning space-based solar power from concept to reality requires overcoming several technical, economic, and logistical challenges. You’ll need efficient orbital logistics to deploy and maintain satellite arrays, ensuring they stay aligned and functional. Power storage becomes critical, as energy collected during peak sunlight must be stored for continuous transmission, especially during nighttime or cloud cover. Developing lightweight, durable materials will reduce launch costs and improve satellite longevity. Advances in wireless power transfer must maximize efficiency to ensure minimal energy loss. Additionally, establishing ground receiving stations that can handle high-power beams safely is essential. Overcoming these hurdles involves coordinated efforts in engineering, policy, and funding. With progress in orbital logistics and power storage solutions, moving toward practical implementation becomes increasingly achievable.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Would Space-Based Solar Power Cost to Implement Globally?
You wonder about the cost estimation and economic feasibility of implementing space-based solar power globally. It’s a complex project, likely costing hundreds of billions to trillions of dollars, depending on the technology and scale. While initial investments are high, the potential for continuous clean energy could outweigh costs over time. However, funding, technological advancements, and international cooperation are vital factors in determining whether this approach is economically feasible.
What Countries Are Leading in Space Solar Power Research?
You’re curious about which countries lead in space solar power research. Currently, the US and China are front-runners, investing heavily in international collaboration and private sector engagement. Europe also plays a significant role, with initiatives fostering cross-border partnerships. These nations recognize the potential of space-based solar energy, pushing innovation through government programs and private companies, aiming to make this renewable source a reality.
How Secure Is Wireless Energy Transmission From Space?
Did you know wireless energy transmission from space has been tested with over 90% efficiency? You might wonder about its security—current research shows that space interference and hacking vulnerabilities are minimal, thanks to advanced encryption and shielding. While no system is completely invulnerable, engineers continuously improve security measures, making space-based power transmission a promising, safe way to deliver clean energy without significant risks of interference or hacking.
Can Space Solar Power Supply Energy During Lunar or Mars Missions?
You wonder if space solar power can supply energy during lunar or Mars missions. It’s promising since space-based solar arrays can generate continuous lunar energy and Mars power, regardless of day-night cycles or weather. Using microwave or laser beams, you could transmit this energy directly to lunar bases or Mars habitats, providing a reliable power source. This technology could revolutionize space exploration by ensuring consistent energy supply beyond Earth.
What Are the Long-Term Environmental Impacts of Space Solar Farms?
Imagine vast space solar farms orbiting Earth, capturing sunlight to beam down energy. You might worry about space debris accumulating and causing collisions, or potential planetary impacts from large structures. Long-term, these impacts could threaten satellite operations or alter Earth’s environment. While promising, you should consider the environmental consequences carefully, ensuring sustainable practices that minimize debris and planetary risks as space-based solar power expands.
Conclusion
Now that you see how space-based solar power could revolutionize energy, are you ready to imagine a future where clean, endless power beams down from above? With ongoing projects and technological leaps, that future isn’t far off. By overcoming challenges and embracing innovation, you can be part of a world powered by the sun’s limitless energy, stored in space and delivered safely to Earth. Isn’t it time we harnessed the sun’s true potential?