Deep-sea hydrothermal vents hold astonishing secrets about life in extreme conditions. Here, organisms thrive in total darkness, high pressure, and intense heat, relying on chemosynthesis instead of sunlight for energy. Unique adaptations, like specialized proteins and symbiotic relationships, help these creatures survive. The nutrient-rich environment supports diverse ecosystems, revealing the interconnectedness of life. By exploring these incredible habitats, you can uncover insights about resilience and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Key Takeaways
- Deep-sea hydrothermal vents create unique ecosystems in extreme conditions, fostering diverse life forms adapted to heat and pressure.
- Organisms like giant tube worms rely on symbiotic bacteria that perform chemosynthesis, converting vent chemicals into energy.
- The mixing of cold nutrient-rich water and hot vent fluids supports complex food webs, with bacteria as the primary energy source.
- Studying these ecosystems enhances our understanding of biological resilience and challenges traditional views on habitable environments beyond Earth.
- Research on hydrothermal vents can inform exploration strategies and contribute to advancements in safety measures for extreme environments, including standby generators.
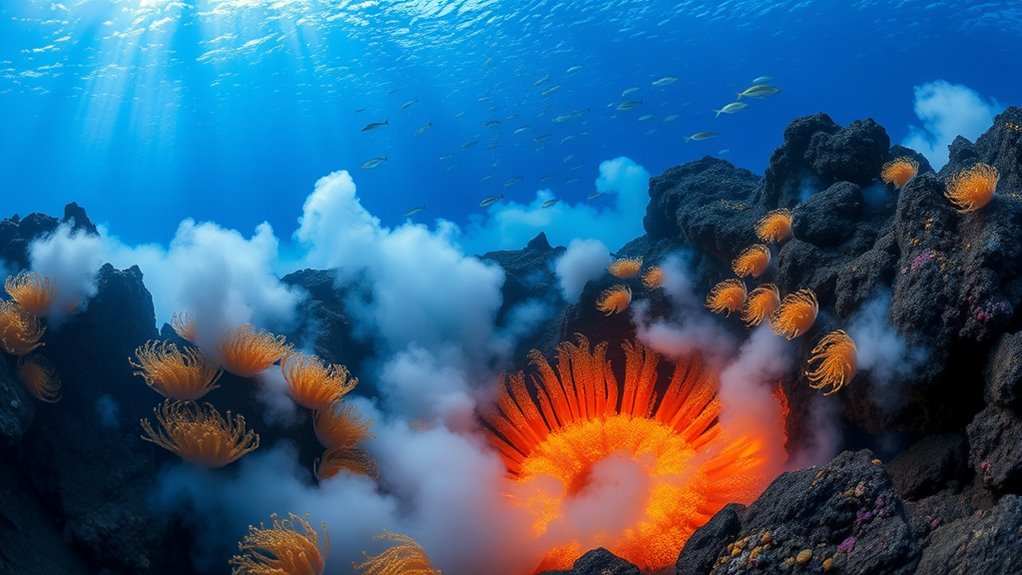

Have you ever wondered about the mysterious ecosystems thriving in the depths of the ocean? Deep-sea hydrothermal vents are some of the most fascinating environments on our planet. As you explore these underwater realms, you’ll discover a world teeming with life, existing in conditions that seem utterly inhospitable. The intense heat, high pressure, and complete darkness make these ecosystems unique, yet they’re home to an array of organisms that have adapted in extraordinary ways.
When you think about life in extreme environments, extremophile adaptations come to mind. These remarkable organisms have evolved specialized traits that enable them to flourish where most life forms wouldn’t stand a chance. For instance, giant tube worms rely on symbiotic bacteria to convert the chemicals spewing from the vents into energy. This process, known as chemosynthesis, replaces the more familiar photosynthesis used by surface plants. You’ll find other extremophiles here, too, like certain species of shrimp and clams, which thrive in water temperatures exceeding 350 degrees Fahrenheit. Their secret? Unique proteins that prevent their cells from denaturing in such extreme conditions.
Understanding vent ecosystem dynamics is essential to appreciating these underwater wonders. The vents release mineral-rich fluids that create a unique habitat. As cold, nutrient-rich water mixes with the hot vent water, it fosters a rich tapestry of life. The interplay between these elements supports a complex food web, where each species plays a vital role. For example, the bacteria at the base of the food chain provide energy for larger organisms, ensuring a steady supply of nutrients throughout the ecosystem. As you explore deeper into this world, you’ll see how interconnected life is, even in the most isolated corners of the ocean.
Understanding the dynamics of vent ecosystems reveals the intricate connections that sustain life in the ocean’s depths.
Exploring hydrothermal vents also raises questions about our own planet’s history and the potential for life beyond Earth. The extremophile adaptations you observe here challenge your understanding of what life can be. If organisms can thrive in such harsh conditions, could similar life exist on other celestial bodies, like Europa or Enceladus? As scientists continue to study these fascinating ecosystems, they reveal secrets that not only enhance our knowledge of biology but also inspire future explorations beyond our planet. Moreover, the study of these ecosystems can provide insights into standby generator safety and preparation for extreme environments on Earth.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Scientists Discover New Hydrothermal Vent Locations?
Scientists discover new hydrothermal vent locations by using advanced mapping techniques and deep sea sensors. They deploy remotely operated vehicles equipped with sonar and cameras to create detailed maps of the ocean floor. These tools help identify anomalies that signal potential vent sites. Additionally, they collect water samples to analyze chemical signatures associated with hydrothermal activity. By combining these methods, you can uncover hidden vent locations and expand our understanding of these unique ecosystems.
What Types of Organisms Thrive Near Hydrothermal Vents?
In the depths of the ocean, where life seems impossible, extremophile species thrive in vibrant vent ecosystems. These remarkable organisms, like tube worms and giant clams, flourish in the extreme temperatures and pressures found near hydrothermal vents. They rely on chemosynthesis, converting chemicals from the vent fluids into energy, creating a bustling community. If you plunge into this underwater world, you’ll witness how life adapts and thrives in the most unlikely places.
Can Hydrothermal Vents Affect Global Climate Change?
Yes, hydrothermal vents can affect global climate change. They play a role in the carbon cycle by releasing carbon dioxide and methane, which can influence atmospheric composition. While these emissions might seem minor compared to human activities, they contribute to the overall climate impact. By studying these vents, you can gain insights into natural processes that regulate greenhouse gases, helping you understand the delicate balance between oceanic systems and climate change.
Are Hydrothermal Vents Dangerous for Human Exploration?
Yes, hydrothermal vents can be dangerous for human exploration. Did you know that temperatures around these vents can reach up to 400 degrees Celsius? This extreme heat poses serious vent safety risks, along with the potential for toxic gas emissions and sudden eruptions. When you venture into these deep-sea environments, you must be aware of these exploration risks and take necessary precautions to guarantee your safety.
What Technologies Are Used to Study These Vents?
To study hydrothermal vents, you’ll find researchers using remote sensing technologies and autonomous vehicles. Remote sensing helps gather data from the surface, allowing scientists to identify vent locations and monitor changes over time. Autonomous vehicles, like underwater drones, dive deep into the ocean, collecting samples and capturing high-resolution images. These tools provide vital insights into the unique ecosystems around the vents, enhancing our understanding of these extreme environments without direct human presence.
Conclusion
As you delve into the mysteries of deep-sea hydrothermal vents, you’re not just skimming the surface; you’re plunging into a world where life thrives against all odds. These underwater geysers whisper secrets of resilience and adaptation, painting a vivid tapestry of existence in the darkness. So, let curiosity guide your journey, and may the wonders of the ocean’s depths spark a flame of discovery in your heart, igniting a passion for the unseen marvels of our planet.