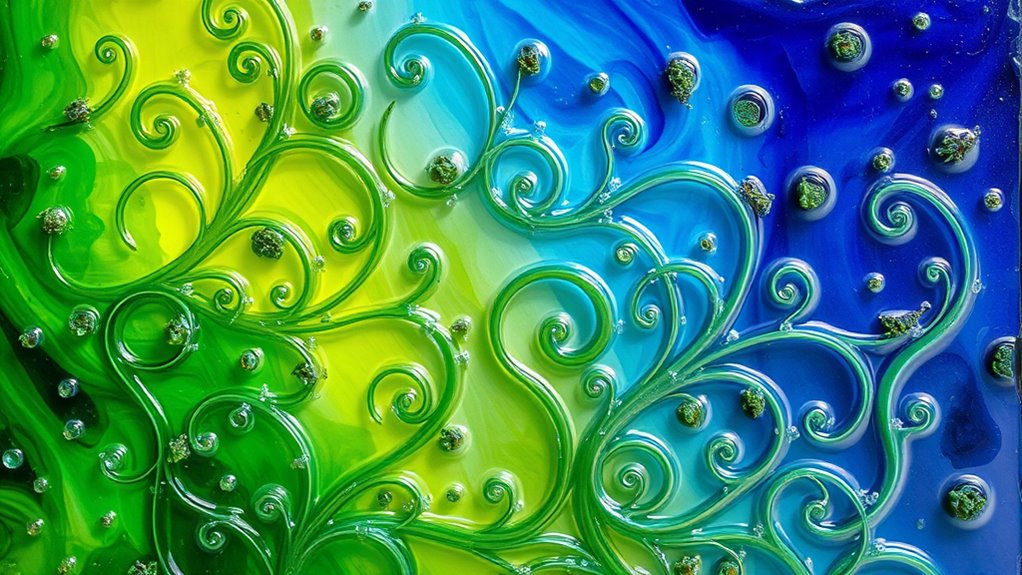
Biofabricated art uses living microorganisms, like bacteria and fungi, as dynamic canvases. These artworks grow and change over time, responding to their environment with shifting colors and patterns. You’ll see how these living sculptures encourage a deeper connection with nature while challenging traditional views of creativity. It’s an exciting blend of artistry and biology that transforms the way you think about art. You’ll discover even more fascinating aspects of this evolving art form.
Key Takeaways
- Biofabricated art utilizes living microorganisms to create dynamic, evolving visual works that challenge traditional artistic boundaries.
- Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi are cultivated to produce vibrant colors and intricate patterns in artworks.
- Living sculptures respond to environmental factors, changing their appearance and engaging viewers in real-time.
- This art form fosters a dialogue between artists, living organisms, and nature, redefining creativity and expression.
- Biofabricated art promotes sustainability and raises ethical questions about the intersection of life and artistic practice.

What if art could grow instead of just being crafted? Imagine walking into a gallery and encountering a piece that evolves right before your eyes. This isn’t just a fantasy; it’s the exciting domain of biofabricated art, where artists use living organisms to create stunning microbial paintings and dynamic living sculptures. This innovative approach transforms how you perceive art, blending creativity with biology.
Imagine stepping into a gallery where art grows and evolves, blending creativity with the living beauty of biofabricated creations.
In biofabricated art, microorganisms like bacteria and fungi become the artists’ tools. These tiny life forms can produce vivid colors and intricate patterns, turning your traditional understanding of painting on its head. Instead of relying on paint from a tube, artists cultivate these microorganisms in specific environments to achieve desired visual effects. You’d be amazed to see how these living paints shift and change, responding to their surroundings and creating art that’s alive in more ways than one.
Living sculptures, another fascinating aspect of this movement, take the concept a step further. Instead of static forms, these sculptures can grow, decay, and even flourish based on their environment. Picture a sculpture that thrives under certain light conditions, its colors deepening or fading as the day goes on. You can witness the cycle of life in real-time, making the experience of viewing art uniquely personal and interactive.
Engaging with biofabricated art challenges your preconceived notions about creativity. It pushes you to contemplate what it means for something to be alive and how that life can contribute to artistic expression. You might find yourself questioning the boundaries between art and nature, realizing that each piece is a collaboration between the artist and the organisms they cultivate. It’s a dialogue, a dance of creation where both the artist and the microbes play essential roles.
As this art form gains traction, you’ll likely see more exhibitions showcasing these living canvases. Artists are experimenting with various microorganisms, exploring how they can manipulate their growth and behavior to produce compelling works. This movement not only celebrates the beauty of life but also raises questions about sustainability and our relationship with nature.
In the end, biofabricated art invites you to reconsider the very essence of art itself. It’s a vibrant reminder that creativity can flourish in the most unexpected forms, urging you to embrace the ever-changing nature of life and art.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Artists Obtain Microorganisms for Biofabrication?
Artists often obtain microorganisms through various sourcing methods, such as isolating them from nature or purchasing them from specialized suppliers. They may use biofabrication techniques like culturing, which involves growing microorganisms in controlled environments to achieve desired characteristics. You might also explore collaborations with scientists or institutions that focus on microbiology. By tapping into these resources, you can effectively source the microorganisms needed for your unique biofabricated projects.
Are Biofabricated Artworks Safe for the Environment?
Yes, biofabricated artworks can be safe for the environment, much like a thriving garden nurtured by nature. When artists carefully select microorganisms, they consider their ecological safety and environmental impact. These living materials often break down naturally, reducing waste compared to traditional art supplies. By promoting sustainability and using renewable resources, you contribute to a healthier planet, allowing creativity to blossom without harming the ecosystems we cherish.
Can Biofabricated Art Be Preserved Long-Term?
Yes, biofabricated art can be preserved long-term, but it comes with longevity challenges. You’ll need to explore various preservation techniques, such as refrigeration or embedding in protective materials, to maintain its integrity. Regular monitoring is essential, as environmental factors can impact the artwork’s condition. By understanding these challenges and employing the right techniques, you can enhance the lifespan of your biofabricated creations and enjoy them for years to come.
What Tools Are Needed for Creating Biofabricated Art?
To create biofabricated art, you’ll need specific tools like a well-designed bioreactor and microbial cultivation techniques. A bioreactor allows you to control environmental conditions for maximum growth, while microbial cultivation techniques help you manipulate the microorganisms effectively. You’ll also benefit from tools for monitoring pH, temperature, and nutrient levels, plus materials for supporting the art’s structure. With these essentials, you can release your creativity in innovative and sustainable ways.
How Do You Care for Biofabricated Artworks?
To care for biofabricated artworks, you need to maintain a controlled environment, ensuring proper humidity and temperature. You should regularly monitor for any signs of decay or contamination. Ethical considerations come into play, as you want to avoid harming the microorganisms involved. Use conservation techniques, like gentle cleaning and proper lighting, to preserve the integrity of the artwork. Always handle with care to keep your living canvas vibrant and healthy.
Conclusion
Biofabricated art is revolutionizing the way we think about creativity and sustainability. Did you know that by 2025, the global biofabrication market is expected to reach over $10 billion? This shift not only showcases the beauty of living organisms but also highlights the potential for eco-friendly practices in the art world. Embracing these living canvases opens up exciting possibilities for artists, pushing boundaries and inspiring future generations to blend science with creativity in innovative ways.